The 10 Engines That Powered the World

Human history is extremely vast, but when you're studying it, you find some pivotal moments that changed everything forever. Usually, they're inventions that completely changed the way we do things, and engines have always helped make a huge leap into new eras.
You might be thinking about the Industrial Revolution and the use of steam engines to power factories during a very particular time in our history, but that's only one of the engines that simplified our lives. Over the centuries, great minds have worked on improving the way we get energy for our houses, vehicles, and appliances. The focus might have changed over the years, but the improvements gave us some of the best machinery in all of history.
The principles behind engines are pretty straightforward, but the needs of society are the ones setting the winds of change. So, here are the 10 engines that powered the world, including those that will make our future.
Turboprop Engine
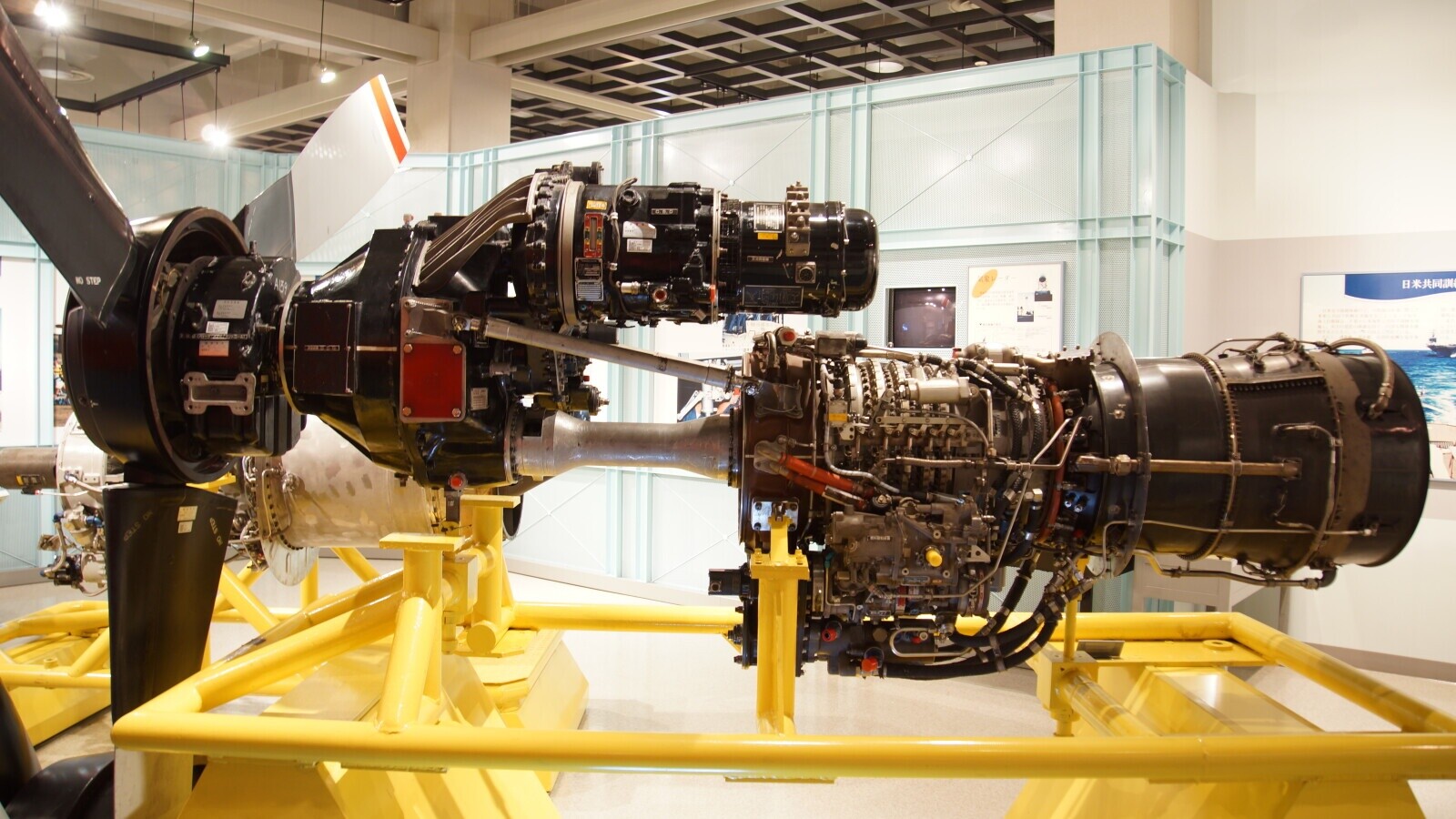

These gas-turbine engines are usually used to drive aircraft propellers. While the first designs were published in the late 1920s, the first turboprop engine was built around 1945. While the jet velocity of the propeller is rather low, it had a big impact on aviation.
Steam Engine
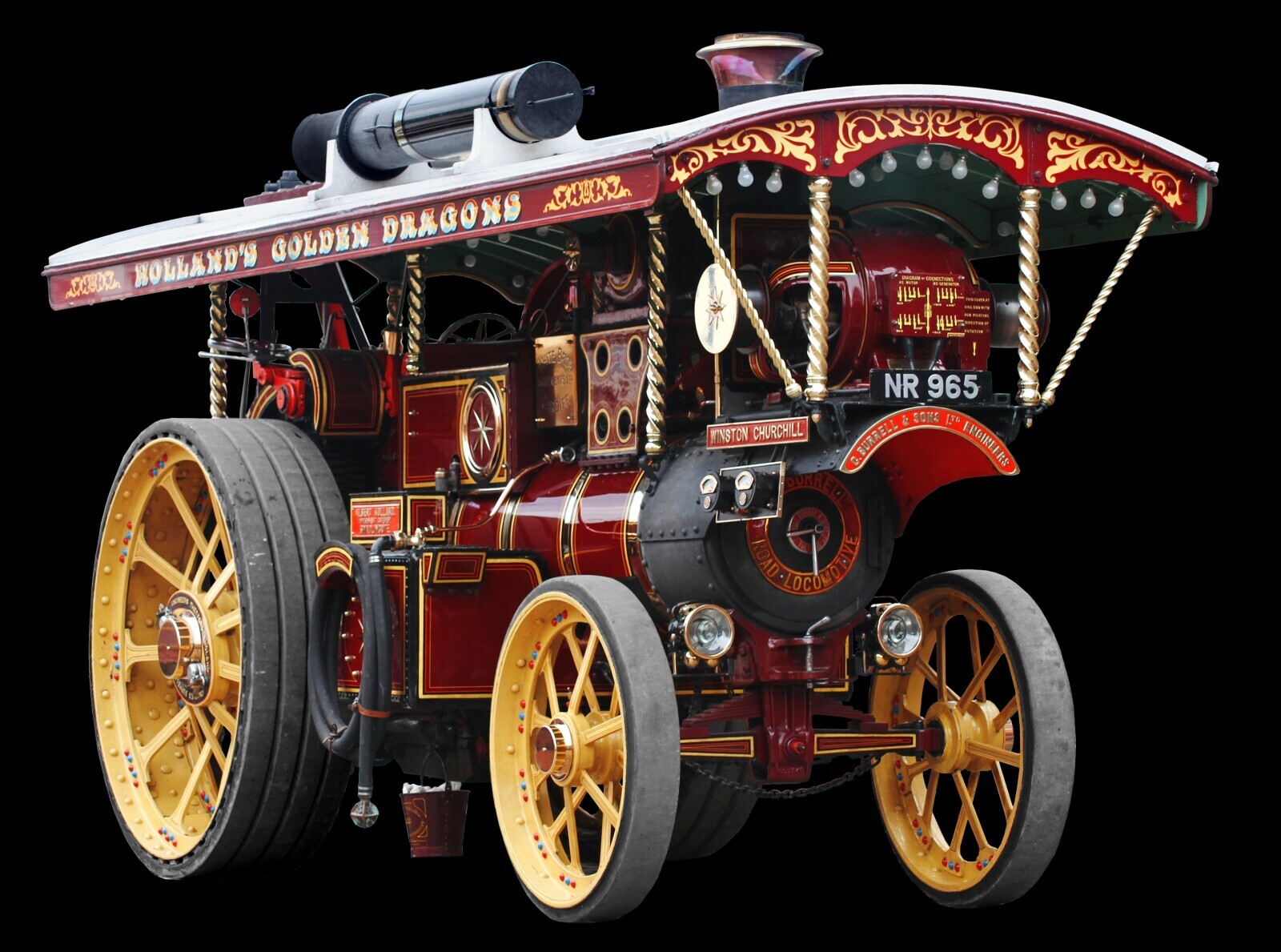

Probably the best-known engine in history due to the Industrial Revolution, but it's rarely around anymore. This type of heat engine has been in the minds of engineers and mathematicians since Ancient Greece. The first ones were built in the 1600s, but changed everything during the 1700s, powering the factories of tomorrow.
Pneumatic Motor
Also known as an air motor or compressed-air engine, it uses compressed air to do its mechanical work. This type of engine is widely used in the hand-held tool industry, but it's used in pretty much everything, including modern robots.
Molecular Motor

Not exactly ‘invented’ by mankind, but all humans have engines that turn substrate into energy to keep on living and doing activities. The best part is that science figured out a way to create these engines by studying the real thing, so we have tons of information on how they work and what they need to do it.
Jet Engine

Jet engines are reaction engines, which means that they produce thrust by expelling reaction mass or reaction propulsion. This internal combustion engine was also in the minds of intellectuals in Ancient Egypt, but technology wasn't there until the 20th Century. Jet engines power jet aircraft, cruise missiles, spaceflight, and military missiles, among other things.
Internal combustion engine
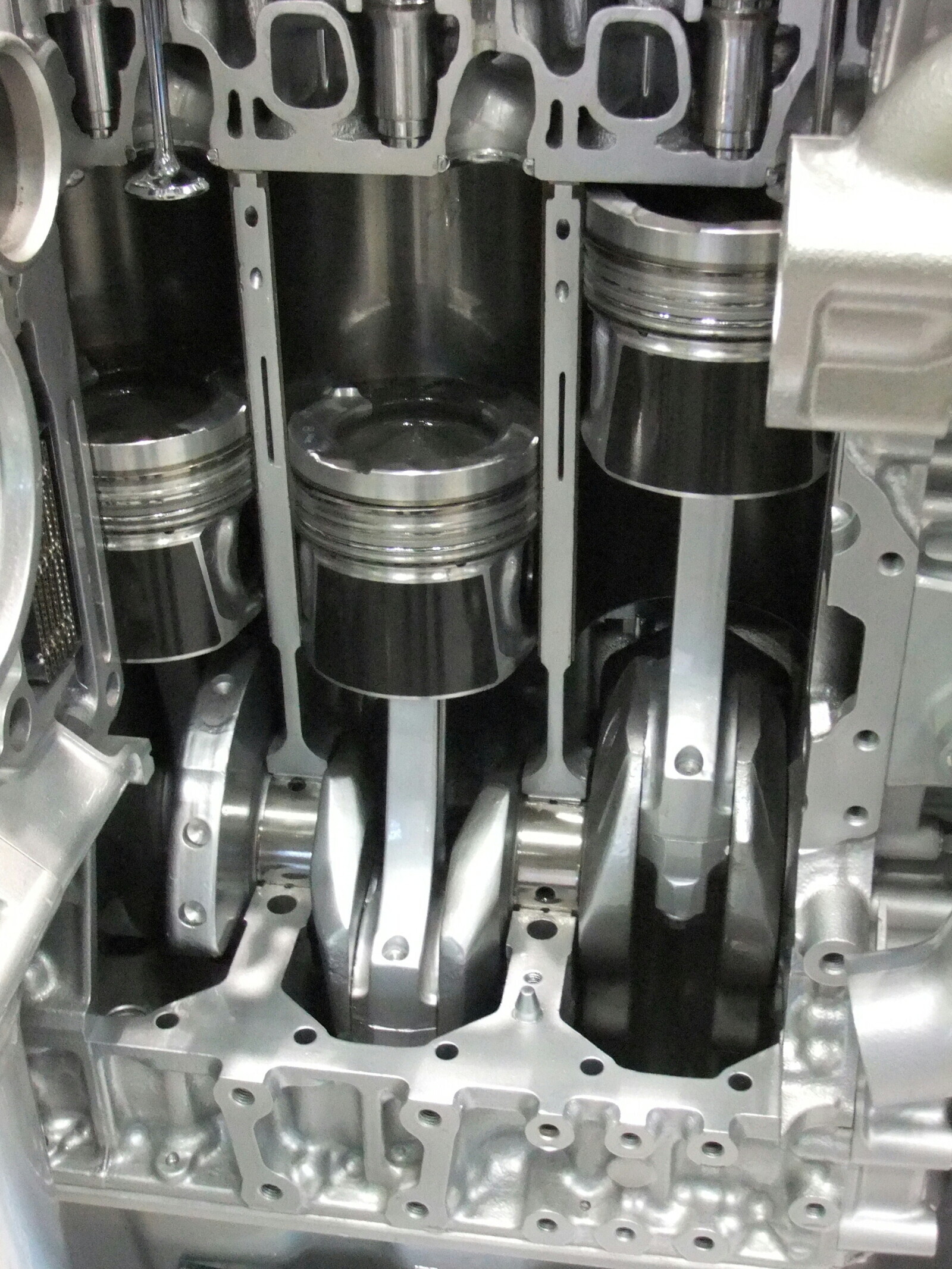

Probably the one you think when you say ‘engine.' The expansion of the high-temperature and high-pressure gases produced by combustion applies direct force to components of the engine like pistons and turbines. The first engine of this type was the Otto engine, designed in 1876, and it's now the most common when it comes to vehicles of all shapes and sizes.
Hydraulic Motor

These engines turn hydraulic pressure into different movements. Basically, there's a closed hydraulic circuit that turns the liquid's flow into a different energy.
External Combustion Engine

These are, of course, similar to the internal combustion engines, but the heating comes from an external source. Electric and steam engines are part of this wide group.
Electric Motor

Electric motors turn electrical power into mechanical energy to power. They're actually the opposite of an electrical generator, and they're taking over fuel-based engines all over the world.
Thermoacoustic Heat Engine
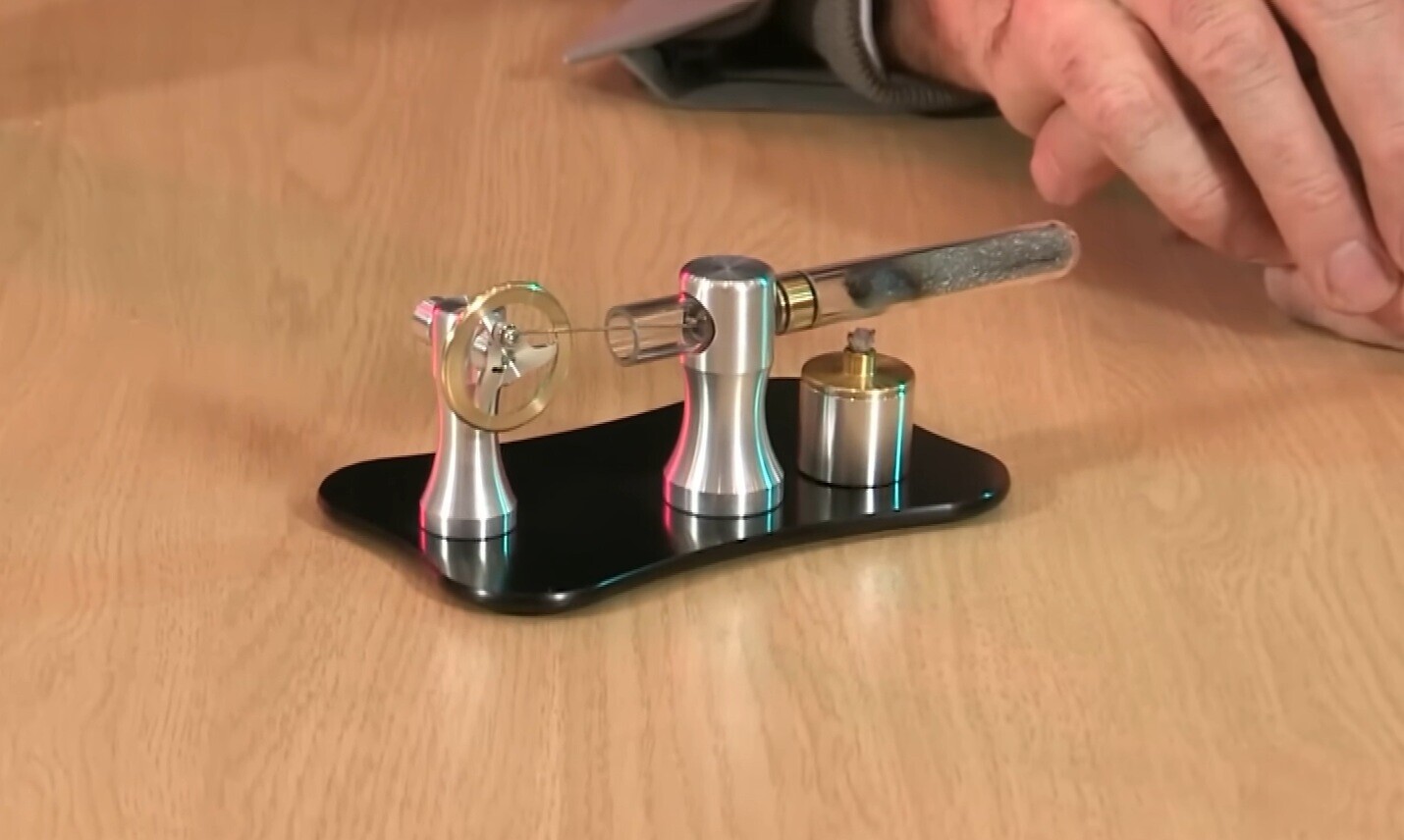

These unique engines use sound waves to pump heat from one place to another. Or the other way around, they use a heat difference to produce sound waves that can be turned into electricity. It has very specific uses, especially in the cryogenic industry.